Benefits of Using Requirements During Test Management
Requirements are specific, pre-defined descriptions of a feature, capability, or constraint that software must possess to meet the needs of its users. Along with risks, requirements are often the starting point in test case design, allowing quality managers to directly validate the presence of a feature or functionality using a corresponding test.

The quality and detail put into capturing and recording requirements will directly impact how well test cases are able to validate stakeholder needs are met. Poor requirement definitions equal poor test cases.
Why Use Requirements?
Software requirements are crucial for guiding the development and testing processes. Therefore, clear and concise requirements will help to:
- Define stakeholder needs before testing begins
- Set clear project goals
- Structure your test design
- Validate test results
- Report and communicate test progress and coverage
Types of Requirements
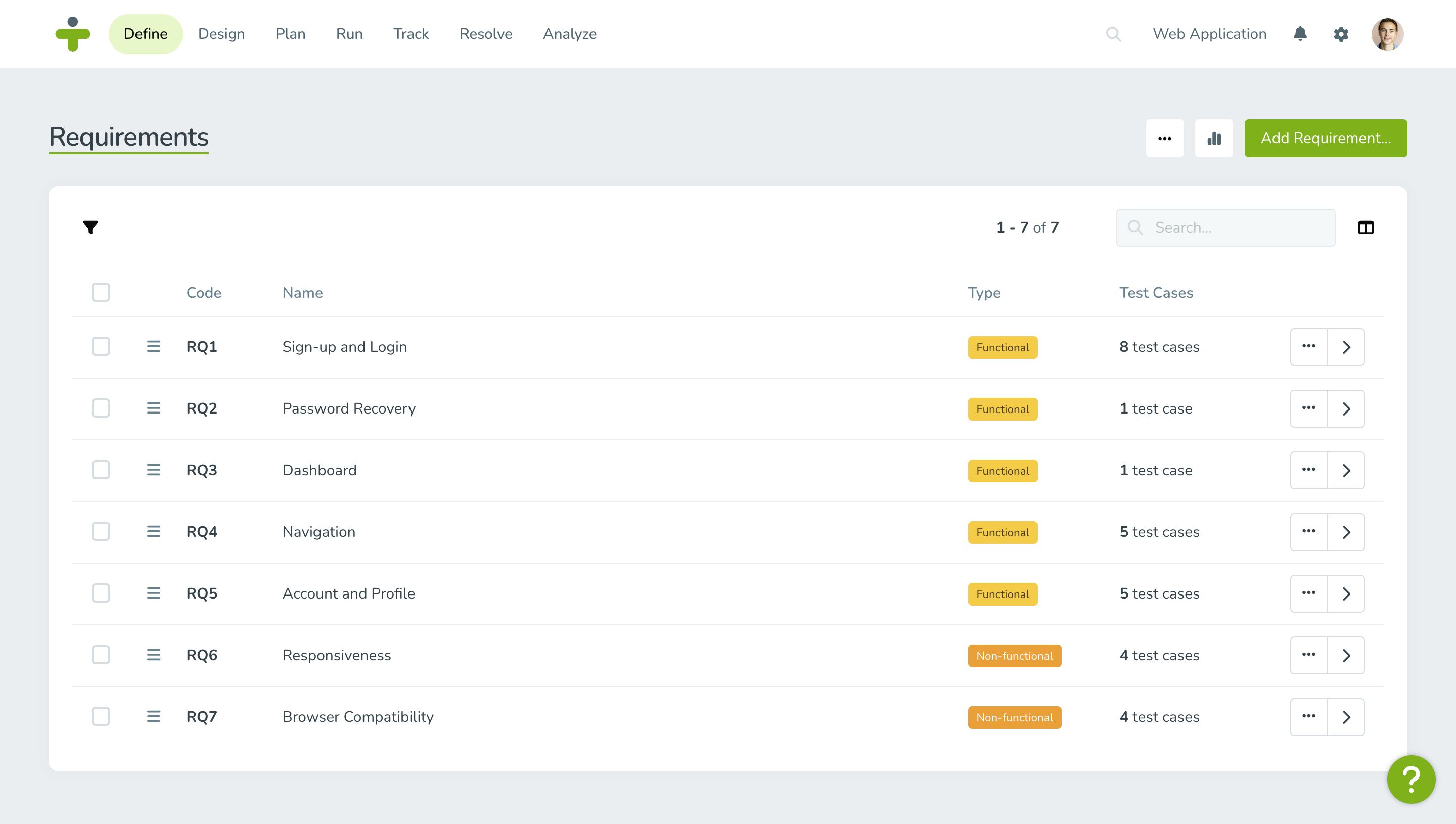
Software requirements can be categorized into various types, including:
- Functional Requirements: These describe the specific functionalities or features that the software must provide like login authentication or report generation.
- Non-functional Requirements: These specify the qualities or attributes of the software, such as performance, security, reliability, and usability.
- User and Business Requirements: These represent software expectations from the perspective of the end user, describing what the software system is expected to accomplish to meet user needs.
- System Requirements: These specify the characteristics of the overall system, including hardware, software, and network requirements so the software can operate effectively.
- Regulatory Requirements: In some industries, software must comply with specific regulations or standards.
Example Requirements
Some common requirements include:
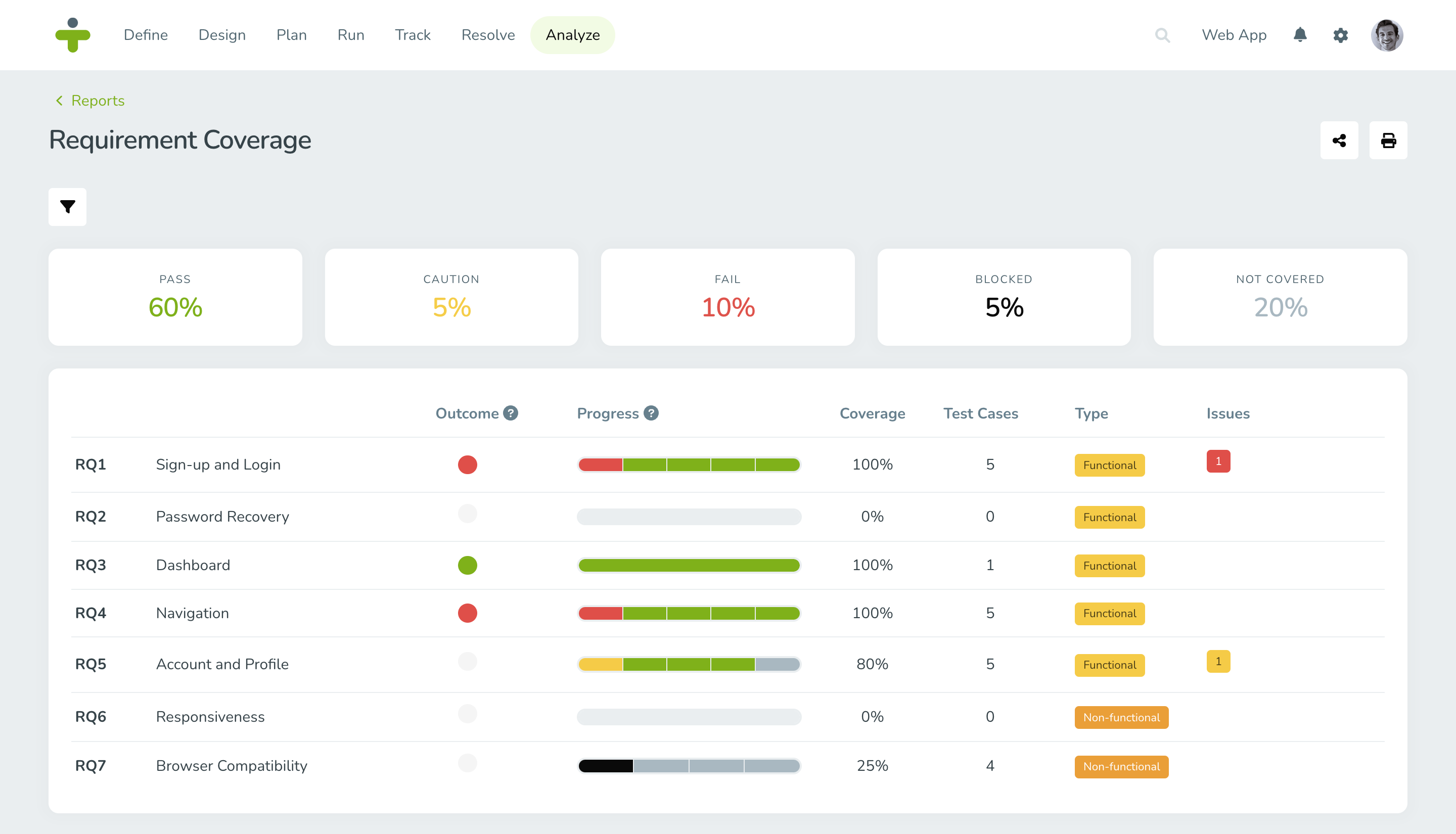
- User Registration: The system shall provide a user registration functionality,
allowing individuals to create an account with a valid email address. - Password Recovery: The system shall allow users to recover their password in case of forgotten credentials.
- Browser Compatibility: The system shall be compatible with major web browsers to ensure a consistent user experience.
Tips and Best Practices for Writing Requirements
Some recommendations for defining and implementing requirements include:
- Simplify Classification
Classify requirements into distinct types (functional, non-functional, business) using standardized schemes for clarity, consistency, and holistic evaluation.
- Prioritize Requirement Review
Prioritize reviewing high-impact requirements to align testing efforts with critical project objectives and to help identify and mitigate risks early.
- Utilize Requirements Management Tools
Use a centralized tool that facilitates filtering and tracing requirements to streamline test case selection, execution, and results analysis based.
- Use Clear Nomenclature
Use concise naming conventions and standardized terminology to ensure universal understanding.
Getting Started in TestMonitor
TestMonitor provides a robust platform for defining requirements and risks like a pro. To learn more about defining requirements in TestMonitor, refer to our Knowledge Base article How to Use Requirements.
Table of Contents
You May Also Like
These Related Stories
Effective Naming Conventions in TestMonitor: Best Practices
.png)
The Importance of Risk Management During Software Testing